|
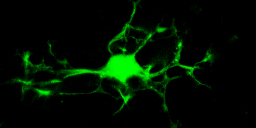
CXCL12-abundant reticular cells as a microenvironmental niche in bone marrow B6;129P2-Cxcl12<tm2Tng>/TngRbrc (RBRC04200)B6;129P2-Cxcr4<tm2Tng>/TngRbrc (RBRC04198)Courtesy of Takashi Nagasawa, M.D., Ph.D. Cell bodies and processes of CXCL12-abundant reticular (CAR) cells, which create a niche for hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs), can be observed in the bone marrow of CXCL12-GFP knock-in mice. |
| CXC chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12), also known as stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-1 or pre-B cell growth-stimulating factor (PBSF) was characterized initially as a growth factor for B cell precursor clones. CXCL12 stimulation is mediated by the G protein-coupled receptor CXCR4. Studies using conventional and conditional knockout mice revealed that CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling has an essential role in hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) maintenance, B cell and germ cell development, neurogenesis, cardiogenesis, and vascular formation [1-4]. Nagasawa and colleagues have revealed the role of CXCL12-abundant reticular (CAR) cells, which are a population of stromal cells that are scattered throughout bone marrow and express high levels of CXCL12 [5, 6]. Recently, they determined a critical role for CAR cells as a microenvironmental niche for HSCs and lymphoid and erythroid progenitors [7-9]. Analyses of CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling in vivo will clarify the molecular mechanisms underlying microenvironmental niche formation in mammals. |
| Depositor | : | Takashi Nagasawa, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Immunobiology and Hematology Institute for Frontier Medical Sciences, Kyoto University |
|
| Strain name | : | B6;129P2-Cxcl12<tm2Tng>/TngRbrc | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC04200 | |
| Strain name | : | B6;129P2-Cxcr4<tm2Tng>/TngRbrc | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC04198 | |
| Related strains | : | B6;129P2-Cxcr4<tm1Tng>/TngRbrc RBRC04197 B6;129P2-Cxcl12<tm1Tng>/TngRbrc RBRC04199 C57BL/6-Tg(Tie2-Cxcl12)1Tng/TngRbrc RBRC04201 |
|
| Model to human diseases | : | HIV-1, SUSCEPTIBILITY TO OMIM ID: 609423 WHIM SYNDROME OMIM ID: 193670 |
|
| References | : | [1] | Ara T, Tokoyoda K, Sugiyama T, Egawa T, Kawabata K, Nagasawa T. Long-term hematopoietic stem cells require stromal cell-derived factor-1 for colonizing bone marrow during ontogeny. Immunity; 19(2):257-67, 2003. |
| [2] | Kohara H, Omatsu Y, Sugiyama T, Noda M, Fujii N, Nagasawa T. Development of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in bone marrow stromal cell niches requires CXCL12-CXCR4 chemokine signaling. Blood; 110(13):4153-60, 2007. | ||
| [3] | Noda M, Omatsu Y, Sugiyama T, Oishi S, Fujii N, Nagasawa T. CXCL12-CXCR4 chemokine signaling is essential for NK-cell development in adult mice. Blood; 117(2):451-8, 2011. | ||
| [4] | Nagasawa T. CXC chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12) and its receptor CXCR4. J Mol Med.; 92(5):433-9, 2014. | ||
| [5] | Tokoyoda K, Egawa T, Sugiyama T, Choi BI, Nagasawa T. Cellular niches controlling B lymphocyte behavior within bone marrow during development. Immunity; 20(6):707-18, 2004. | ||
| [6] | Sugiyama T, Kohara H, Noda M, Nagasawa T. Maintenance of the hematopoietic stem cell pool by CXCL12-CXCR4 chemokine signaling in bone marrow stromal cell niches. Immunity; 25(6):977-88, 2006. | ||
| [7] | Omatsu Y, Sugiyama T, Kohara H, Kondoh G, Fujii N, Kohno K, Nagasawa T. The essential functions of adipo-osteogenic progenitors as the hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell niche. Immunity; 33(3):387-99, 2010. | ||
| [8] | Greenbaum A, Hsu YM, Day RB, Schuettpelz LG, Christopher MJ, Borgerding JN, Nagasawa T, Link DC. CXCL12 in early mesenchymal progenitors is required for haematopoietic stem-cell maintenance. Nature; 495(7440):227-30, 2013. | ||
| [9] | Omatsu Y, Seike M, Sugiyama T, Kume T, Nagasawa T. Foxc1 is a critical regulator of haematopoietic stem/progenitor cell niche formation. Nature; 508(7497):536-40, 2014. | ||
| December 2014 Contact: Shinya Ayabe, Ph.D. Experimental Animal Division, RIKEN BioResource Center All materials contained on this site may not be reproduced, distributed, displayed, published or broadcast without the prior permission of the owner of that content. |