|
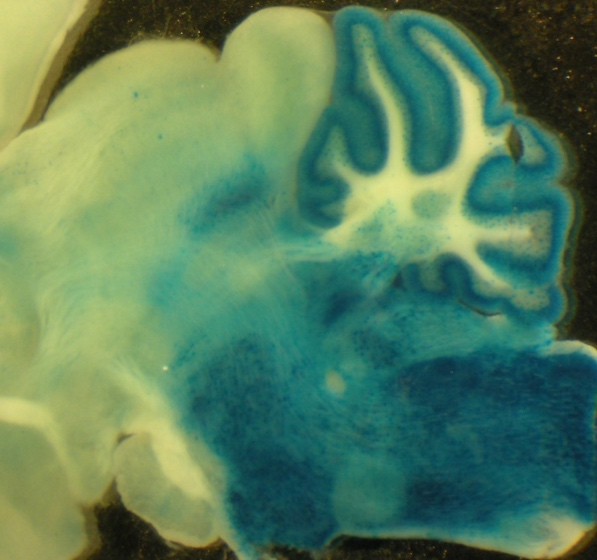
Glycinergic neuron Cre-driver mice C57BL/6-Slc6a5<tm1.1(cre)Ksak> (RBRC10109)Courtesy of Toshikazu Kakizaki, Ph.D. X-gal staining of midbrain and hindbrain sections from adult GLYT2-Cre KI/R26R double transgenic mice. |
|
Glycinergic neuron is a major inhibitory neuron in central nervous system (brainstem, spinal cord, etc.), which control various physiological functions (sensory, motor, respiratory, etc.) depending on the activity of glycine neurotransmitter transportation. GLYT2-Cre KI mice (RBRC10109) is a useful Cre driver strain for glycinergic neuron related research. GLYT2-Cre KI mice express Cre-recombinase under the control of endogenous Glyt2 (Slc6a5) gene promoter. Because GLYT2 (glycine transporter 2) localize to glycinergic neuron, GLYT2 is known to be a specific marker of glycinergic neuron. Depositor (Dr. Kakizaki) and his colleague clarified that GLYT2-Cre KI mice express Cre recombinase in glycinergic neuron by mating experiments with Cre-reporter (R26R) mice and this expression region is colocalized to Glyt2 mRNA expression region. It means that GLYT2-Cre KI mice allow the gene manipulation by Cre/loxP recombination system in glycinergic neuron. GLYT2-Cre KI mice will offer new insight into the functions and mechanisms of glycinergic neuron and glycinergic neurotransmitter in vivo. |
| Depositor | : | Toshikazu Kakizaki, Ph.D. Department of Genetic and Behavioral Neuroscience, Graduate School of Medicine, Gunma University |
|
| Strain name | : | C57BL/6-Slc6a5<tm1.1(cre)Ksak> | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC10109 | |
| Reference | : | Kakizaki T, Sakagami H, Sakimura K, Yanagawa Y. A glycine transporter 2-Cre knock-in mouse line for glycinergic neuron-specific gene manipulation. IBRO Rep.; 3:9-16, 2017. |
|
| December 2019 Saori Mizuno, Ph.D. Contact: Experimental Animal Division, RIKEN BioResource Research Center (animal.brc@riken.jp) All materials contained on this site may not be reproduced, distributed, displayed, published or broadcast without the prior permission of the owner of that content. |