|
February 2021 Mouse of the Month |
Ucp1 in vivo imaging mice
C57BL/6J-Ucp1<em1(iRFP720)Utgr>
|
|
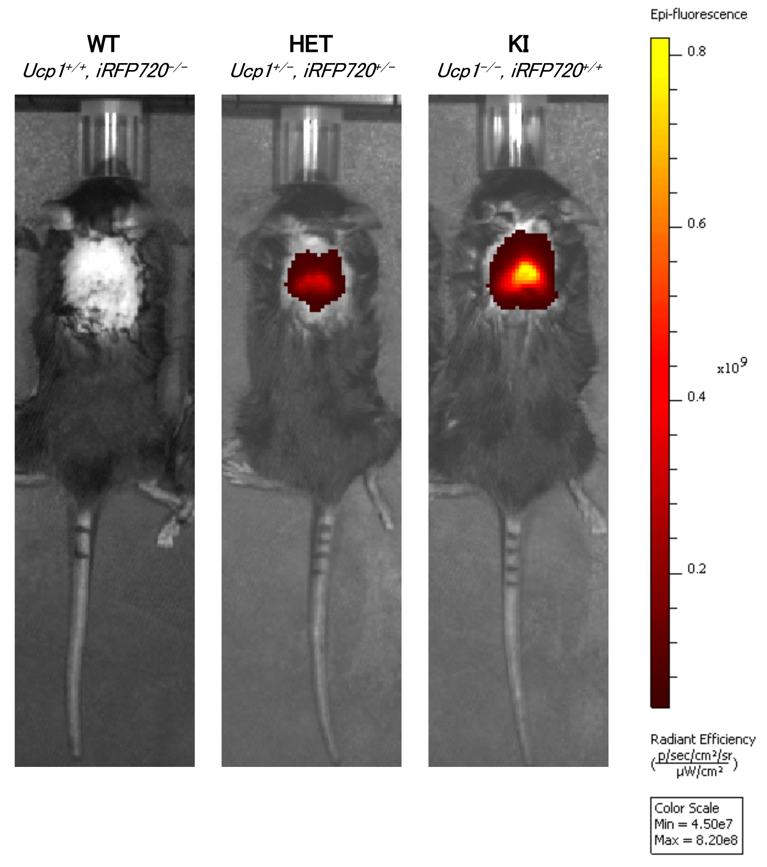
UCP1 (uncoupling protein 1) is a mitochondrial protein that uncouples electron transport system from ATP synthesis as a proton translator at the mitochondrial inner membrane. UCP1 expression is restricted to both brown and beige adipocytes. Due to its ability to radiate heat energy, UCP1 expression is used for an important index for thermogenesis. |
| Depositor | : | Aya Fukuda, Ph.D. University of Tsukuba |
|
| Strain name | : | C57BL/6J-Ucp1<em1(iRFP720)Utgr> | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC10928 | |
| Reference | : | [1] | Fukuda A, Honda S, Fujioka N, Sekiguchi Y, Mizuno S, Miwa Y, Sugiyama F, Hayashi Y, Nishimura K, Hisatake K. Non-invasive in vivo imaging of UCP1 expression in live mice via near-infrared fluorescent protein iRFP720 PLoS One. 2019 Nov 15;14(11):e0225213. |
| February 2021 Saori Mizuno, Ph.D. Contact: Experimental Animal Division, RIKEN BioResource Research Center (animal.brc@riken.jp) All materials contained on this site may not be reproduced, distributed, displayed, published or broadcast without the prior permission of the owner of that content. |