|
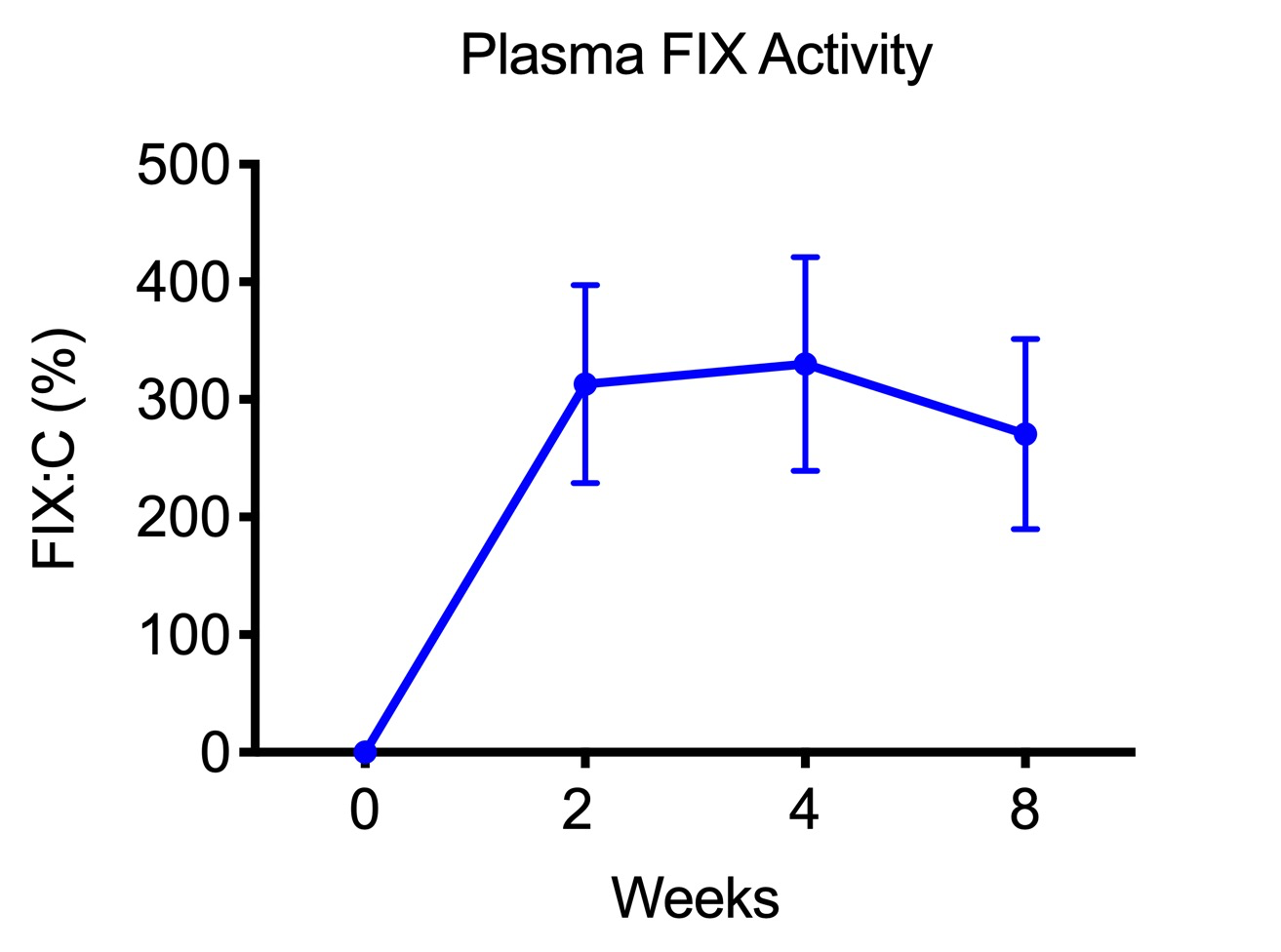
Haemophilia B model mice C57BL/6J-F9<em1Tsuka> (RBRC10062)Courtesy of Tsukasa Ohmori, M.D., Ph.D. Increase in plasma coagulation factor Ⅸ (FIX) by administration of adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector(n=3, Mean±SEM). |
|
Haemophilia B is an X-linked congenital hemorrhagic disease caused by mutations in coagulation factor Ⅸ genes (F9). The treatment is done by replacing the coagulation factors. However, it has some problems to be solved. Because these coagulation factors have extremely short half-life, patients need constant injection. Additionally, it is known that some patients develop antibodies to the coagulation factors. Establishment of new therapies is desired. Haemophilia B model mice (RBRC10062) generated by CRISPR/Cas9 system have 12 bp deletion in exon 8 of F9 gene. This strain shows both bleeding phenotype and a reduction of plasma coagulation factor Ⅸ (FIX) activity, similar to the human condition. Actually, utilizing this model mice, a novel gene therapy strategy with CRISPR/Cas9 system and adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector was reported. This strain will help to develop the cure of haemophilia B. |
| Depositor | : | Tsukasa Ohmori, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry, Jichi Medical University, School of Medicine |
|
| Strain name | : | C57BL/6J-F9<em1Tsuka> | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC10062 | |
| Reference | : | Ohmori T, Nagao Y, Mizukami H, Sakata A Muramatsu SI, Ozawa K, Tominaga SI, Hanazono Y, Nishimura S, Nureki O, Sakata Y. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing via postnatal administration of AAV vector cures haemophilia B mice. Sci Rep.; 7(1):4159., 2017. |
|
| June 2019 Contact: Saori Mizuno, Ph.D. Experimental Animal Division, RIKEN BioResource Research Center All materials contained on this site may not be reproduced, distributed, displayed, published or broadcast without the prior permission of the owner of that content. |