|
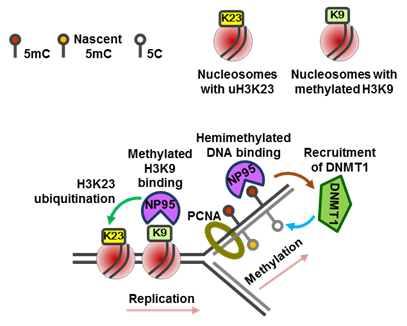
A key factor for epigenetic inheritance of DNA methylation B6.Cg-Uhrf1<tm2.1Hko> (RBRC06536)Courtesy of Haruhiko Koseki, M.D., Ph.D. Epigenetic functions mediated by the multi-domain protein NP95/UHRF1. During replication, NP95 recognizes hemimethylated DNA at the fork and recruits DNMT1 to facilitate conversion into the fully methylated state (shown on the right). NP95 also recognizes nucleosomes containing methylated H3K9 residues and mediates ubiquitination of H3K23 (shown on the left). |
| Epigenetic modifications such as DNA methylation play an important role in regulating gene expression. Methylated DNA recruits methylcytosine (5mC)-binding proteins that in turn promote chromatin condensation, leading to transcriptional repression. DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) is an essential factor for the epigenetic inheritance of DNA methylation patterns, as it mediates the enzymatic conversion of hemi-methylated CpG sites into fully methylated ones at replication foci.
The SET and RING finger-associated (SRA) domain protein NP95 (also known as UHRF1 or ICBP90) plays a crucial role in the maintenance of DNA methylation by binding to hemi-methylated CpGs at replication foci through its SRA domain and recruiting DNMT1 [1]. Recent studies have revealed that NP95 also recognizes methylated H3K9 (histone H3 lysine 9) residues [2] and ubiquitinates histone H3 (K23) [3]. In addition, it has been shown that T-cell-specific Uhrf1/Np95 deficient mice spontaneously develop colitis due to defects in the proliferation and maturation of regulatory T cells through epigenetic silencing of Cdkn1a [4]. A conditional Uhrf1 knockout mouse strain provides an opportunity to clarify the role of the Uhrf1-dependent regulation of DNA methylation in various types of cells and organs. |
| Depositor | : | Haruhiko Koseki, M.D., Ph.D. Laboratory for Developmental Genetics RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences (IMS) |
|
| Strain name | : | B6.Cg-Uhrf1<tm2.1Hko> | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC06536 | |
| References | : | [1] | Sharif J, Muto M, Takebayashi S, Suetake I, Iwamatsu A, Endo TA, Shinga J, Mizutani-Koseki Y, Toyoda T, Okamura K, Tajima S, Mitsuya K, Okano M, Koseki H. The SRA protein Np95 mediates epigenetic inheritance by recruiting Dnmt1 to methylated DNA. Nature; 450(7171):908-12, 2007. |
| [2] | Nishiyama A, Yamaguchi L, Sharif J, Johmura Y, Kawamura T, Nakanishi K, Shimamura S, Arita K, Kodama T, Ishikawa F, Koseki H, Nakanishi M. Uhrf1-dependent H3K23 ubiquitylation couples maintenance DNA methylation and replication. Nature; 502(7470):249-53, 2013. | ||
| [3] | Arita K, Isogai S, Oda T, Unoki M, Sugita K, Sekiyama N, Kuwata K, Hamamoto R, Tochio H, Sato M, Ariyoshi M, Shirakawa M. Recognition of modification status on a histone H3 tail by linked histone reader modules of the epigenetic regulator UHRF1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.; 109(32):12950-5, 2012. | ||
| [4] | Obata Y, Furusawa Y, Endo TA, Sharif J, Takahashi D, Atarashi K, Nakayama M, Onawa S, Fujimura Y, Takahashi M, Ikawa T, Otsubo T, Kawamura YI, Dohi T, Tajima S, Masumoto H, Ohara O, Honda K, Hori S, Ohno H, Koseki H, Hase K. The epigenetic regulator Uhrf1 facilitates the proliferation and maturation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol.; 15(6):571-9, 2014. | ||
| May 2015 Contact: Shinya Ayabe, Ph.D. Experimental Animal Division, RIKEN BioResource Center All materials contained on this site may not be reproduced, distributed, displayed, published or broadcast without the prior permission of the owner of that content. |