|
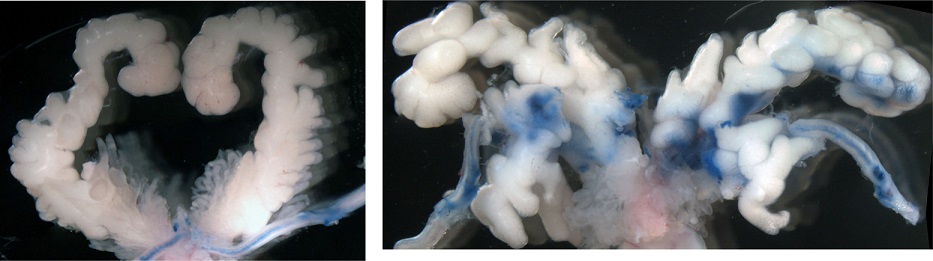
C429S mutation in the mouse β-catenin gene B6(D2)-Ctnnb1<Rgsc1880>/Rbrc (RBRC06154)B6.Cg-Tg(TOPGAL) Ctnnb1<Rgsc1880>/Rbrc (RBRC06153)Staining with trypan blue allows for visualization of the route of sperm. In wild-type males (left panel), the dye was seen in only the vas deferens, while in C429S mutant males (right panel), the dye was also found in the duplicated and enlarged seminal vesicles. It indicated the detoured migration of sperm into the seminal vesicles by the C429S mutation. Upon microscopic observation, sperm were indeed found in the mutant seminal vesicles. (Figures courtesy of Takuya Murata, Ph.D.) |
| β-Catenin is essential for Wnt signaling and cadherin-based cell adhesion. Activating mutations in the human β-catenin gene have been found in cancer, which demonstrates the need to regulate β-catenin expression throughout embryonic development and adulthood. Gondo and colleagues developed a novel β-cateninC429S congenic mouse strain by performing high-throughput mutation screening of an ENU-mutagenized male genomic DNA library [1, 2]. They found that homozygous mutant mice are infertile by natural mating, while the sperm and oocytes of the mutant mice are normal. They observed the abnormal development of the seminal vesicles in males and the vagina in females, and the ins-TOPGAL transgenic reporter visualized abnormal Wnt/β-catenin signaling throughout organogenesis [3, 4]. An interesting point of note in their report is that β-cateninC429S mice showed a limited phenotype even though β-catenin is involved in a broad range of biological systems. This mouse strain revealed new biological functions of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and may provide an opportunity to understand human infertility. |
| Depositor | : | Yoichi Gondo, Ph.D. Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN BioResource Center |
|
| Strain name | : | B6(D2)-Ctnnb1<Rgsc1880>/Rbrc | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC06154 | |
| Strain name | : | B6.Cg-Tg(TOPGAL) Ctnnb1<Rgsc1880>/Rbrc | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC06153 | |
| Related strain name | : | B6.Cg-Tg(TOPGAL)/Rbrc | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC05918 | |
| References | : | [1] | Gondo Y. Trends in large-scale mouse mutagenesis: from genetics to functional genomics. Nat Rev Genet.; 9(10):803-10, 2008. |
| [2] | Gondo Y, Fukumura R, Murata T, Makino S. ENU-based gene-driven mutagenesis in the mouse: a next-generation gene-targeting system. Exp Anim.; 59(5):537-48, 2010. | ||
| [3] | Moriyama A, Kii I, Sunabori T, Kurihara S, Takayama I, Shimazaki M, Tanabe H, Oginuma M, Fukayama M, Matsuzaki Y, Saga Y, Kudo A. GFP transgenic mice reveal active canonical Wnt signal in neonatal brain and in adult liver and spleen. Genesis.; 45(2):90-100, 2007. | ||
| [4] | Murata T, Ishitsuka Y, Karouji K, Kaneda H, Toki H, Nakai Y, Makino S, Fukumura R, Kotaki H, Wakana S, Noda T, Gondo Y. β-catenin(C429S) mice exhibit sterility consequent to spatiotemporally sustained Wnt signalling in the internal genitalia. Sci Rep.; 24:6959, 2014. | ||
| November 2014 Contact: Shinya Ayabe, Ph.D. Experimental Animal Division, RIKEN BioResource Center All materials contained on this site may not be reproduced, distributed, displayed, published or broadcast without the prior permission of the owner of that content. |