|
November 2018 Mouse of the Month |
|
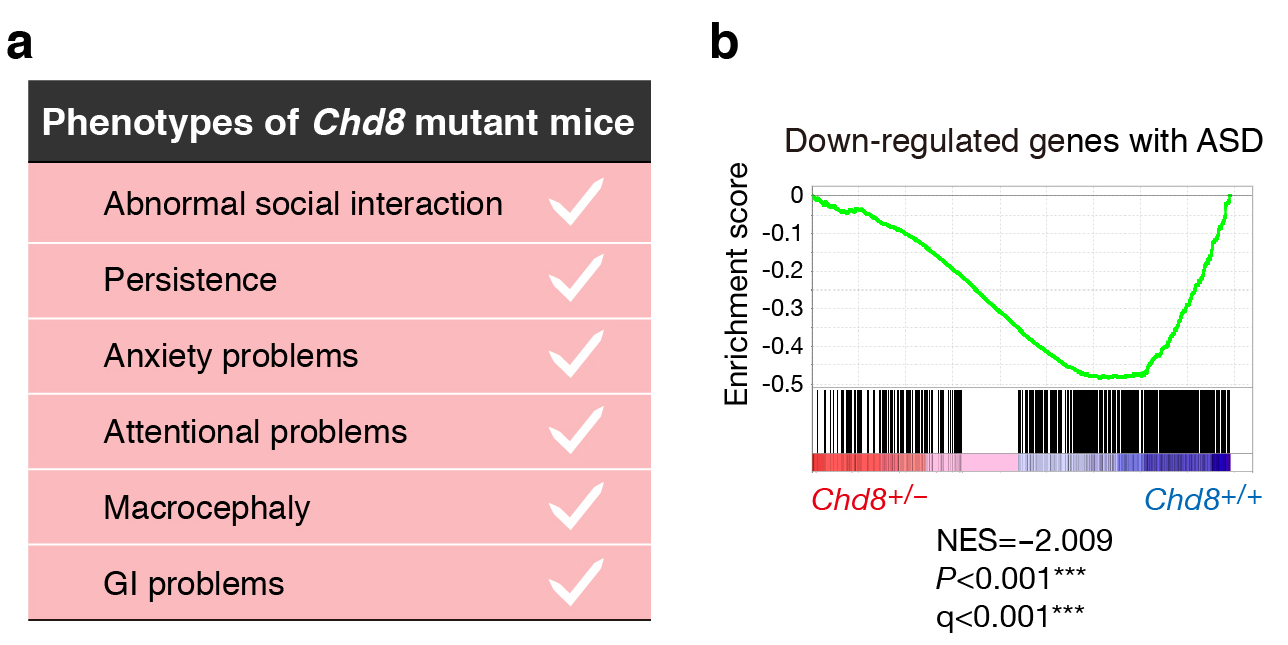
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) model mice B6;129P2-Chd8<tm1Kei> (RBRC09758)B6.129P2-Chd8<tm2.1Kei> (RBRC09759)Courtesy of Keiichi Nakayama, M.D., Ph.D. a, List of detected phenotypes with Chd8 heterozygous mutation in mice. Both Chd8 mutant strains (RBRC09758 and RBRC09759) show similar symptoms found in ASD patients with Chd8 mutation. b, Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) plot of down-regulated genes with ASD. GSEA revealed that genes in which expression is down-regulated in the brain of ASD patients tended to show a similar expression pattern in the brain of Chd8 heterozygous mutant mice. |
|
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a highly prevalent neurodevelopmental disorder. ASD is characterized by difficulties in social communication and social interaction, and by restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior. ASD pathogenic mechanism is suggested to be closely related to genetic factors. Recent exosome sequence analysis for ASD patients revealed many de novo mutations, with chromatin helicase DNA-binding protein 8 (Chd8) being the most frequent mutation site (1, 2, 3). Chd8 is a remarkable gene for ASD research. |
| Depositor | : | Keiichi Nakayama, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology Medical Institute of Bioregulation, Kyushu University |
|
| Strain name | : | B6;129P2-Chd8<tm1Kei> | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC09758 | |
| Strain name | : | B6.129P2-Chd8<tm2.1Kei> | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC09759 | |
| References | : | [1] | O’Roak BJ, Vives L, Girirajan S, Karakoc E, Krumm N, Coe BP, Levy R, Ko A, Lee C, Smith JD, Turner EH, Stanaway IB, Vernot B, Malig M, Baker C, Reilly B, Akey JM, Borenstein E, Rieder MJ, Nickerson DA, Bernier R, Shendure J, Eichler EE. Sporadic autism exomes reveal a highly interconnected protein network of de novo mutations.Nature.; 485(7397): 246-250, 2012. |
| [2] | Talkowski ME, Rosenfeld JA, Blumenthal I, Pillalamarri V, Chiang C, Heilbut A, Ernst C, Hanscom C, Rossin E, Lindgren AM, Pereira S, Ruderfer D, Kirby A, Ripke S, Harris DJ, Lee JH, Ha K, Kim HG, Solomon BD, Gropman AL, Lucente D, Sims K, Ohsumi TK, Borowsky ML, Loranger S, Quade B, Lage K, Miles J, Wu BL, Shen Y, Neale B, Shaffer LG, Daly MJ, Morton CC, Gusella JF. Sequencing chromosomal abnormalities reveals neurodevelopmental loci that confer risk across diagnostic boundaries.Cell.; 149(3): 525-537, 2012. | ||
| [3] | Neale BM, Kou Y, Liu L, Ma’ayan A, Samocha KE, Sabo A, Lin CF, Stevens C, Wang LS, Makarov V, Polak P, Yoon S, Maguire J, Crawford EL, Campbell NG, Geller ET, Valladares O, Schafer C, Liu H, Zhao T, Cai G, Lihm J, Dannenfelser R, Jabado O, Peralta Z, Nagaswamy U, Muzny D, Reid JG, Newsham I, Wu Y, Lewis L, Han Y, Voight BF, Lim E, Rossin E, Kirby A, Flannick J, Fromer M, Shakir K, Fennell T, Garimella K, Banks E, Poplin R, Gabriel S, DePristo M, Wimbish JR, Boone BE, Levy SE, Betancur C, Sunyaev S, Boerwinkle E, Buxbaum JD, Cook EH Jr, Devlin B, Gibbs RA, Roeder K, Schellenberg GD, Sutcliffe JS, Daly MJ. Patterns and rates of exonic de novo mutations in autism spectrum disorders.Nature.; 485(7397): 242-245, 2012. | ||
| [4] | Katayama Y, Nishiyama M, Shoji H, Ohkawa Y, Kawamura A, Sato T, Suyama M, Takumi T, Miyakawa T, Nakayama KI. CHD8 haploinsufficiency results in autistic-like phenotypes in mice.Nature.; 537(7622): 675-679, 2016. | ||
| [5] | Bernier R, Golzio C, Xiong B, Stessman HA, Coe BP, Penn O, Witherspoon K, Gerdts J, Baker C, Vulto-van Silfhout AT, Schuurs-Hoeijmakers JH, Fichera M, Bosco P, Buono S, Alberti A, Failla P, Peeters H, Steyaert J, Vissers LELM, Francescatto L, Mefford HC, Rosenfeld JA, Bakken T, O’Roak BJ, Pawlus M, Moon R, Shendure J, Amaral DG, Lein E, Rankin J, Romano C, de Vries BBA, Katsanis N, Eichler EE. Disruptive CHD8 mutations define a subtype of autism early in development.Cell.; 158(2): 263-276, 2014. | ||
| November 2018 Contact: Saori Mizuno, Ph.D. Experimental Animal Division, RIKEN BioResource Research Center All materials contained on this site may not be reproduced, distributed, displayed, published or broadcast without the prior permission of the owner of that content. |