|
November 2022 Mouse of the Month |
|
RASopathies (RAS/MAPK syndromes) model mice
RASopathies are a group of rare genetic disorders caused by mutations in genes of the Ras-MAPK pathway. |
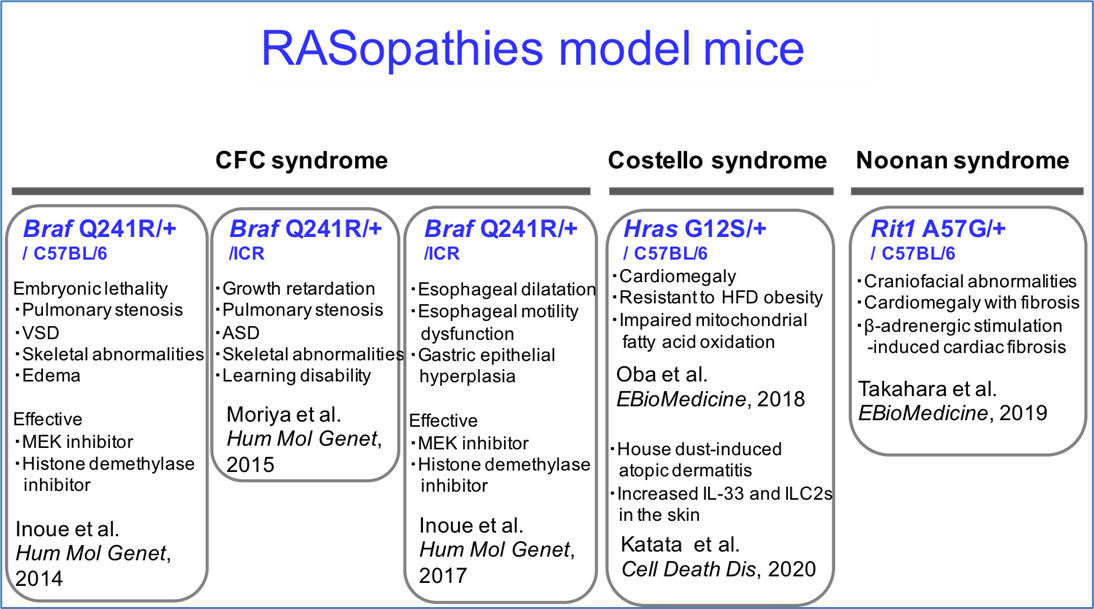
| RASopathies (RAS/MAPK syndromes) are a series of syndromes caused by mutations in genes on RAS/MAPK signaling pathway involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Symptoms such as short stature, cardiac malformation, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, skeletal abnormalities, and carcinogenesis are similar to each other. In addition, since no treatment has been established, these are classified as designated intractable diseases. RIKEN BRC is able to provide model mice for the following three diseases that carry the genetic mutations discovered in the patients. It is expected that these strains will be used to elucidate the pathogenesis of the disease and to develop therapeutic methods. |
|
Cardio-facio-cutaneous (CFC) syndrome (OMIM#115150) model mice
The CFC syndrome model mice are knock-in mice carrying Braf Q241R mutation, which corresponds to BRAF Q257R, the most frequent mutation in patients. BRAF is a serine/threonine kinase present in RAS/MAPK signaling and is also known as a carcinogenic gene. These strains show cardiac disease, skeletal abnormalities, and posterior cervical edema from embryonic development, similar to patients. |
| Strain name: ▪ B6.Cg-Braf<tm1Tumg> (C57BL/6 background)(RBRC09730) ▪ ICR.Cg-Braf<tm1.1Tumg> (ICR background) (RBRC09731) ▪ 129.Cg-Braf<tm1Tumg> (129 background) (RBRC09907) ▪ C.Cg-Braf<tm1Tumg> (BALB/c background) (RBRC09908) |
| References: [1] Gualtieri A, Kyprianou N, Gregory LC, Vignola ML, Nicholson JG, Tan R, Inoue SI, Scagliotti V, Casado P, Blackburn J, Abollo-Jimenez F, Marinelli E, Besser REJ, Högler W, Karen Temple I, Davies JH, Gagunashvili A, Robinson ICAF, Camper SA, Davis SW, Cutillas PR, Gevers EF, Aoki Y, Dattani MT, Gaston-Massuet C. Activating mutations in BRAF disrupt the hypothalamo-pituitary axis leading to hypopituitarism in mice and humans. Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 1;12(1):2028. [2] Inoue SI, Morozumi N, Yoshikiyo K, Maeda H, Aoki Y. C-type natriuretic peptide improves growth retardation in a mouse model of cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2019 Jan 1;28(1):74-83. [3] Inoue SI, Takahara S, Yoshikawa T, Niihori T, Yanai K, Matsubara Y, Aoki Y. Activated Braf induces esophageal dilation and gastric epithelial hyperplasia in mice. Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Dec 1;26(23):4715-4727. [4] Moriya M, Inoue S, Miyagawa-Tomita S, Nakashima Y, Oba D, Niihori T, Hashi M, Ohnishi H, Kure S, Matsubara Y, Aoki Y. Adult mice expressing a Braf Q241R mutation on an ICR/CD-1 background exhibit a cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome phenotype. Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Dec 20;24(25):7349-60. [5] Inoue S, Moriya M, Watanabe Y, Miyagawa-Tomita S, Niihori T, Oba D, Ono M, Kure S, Ogura T, Matsubara Y, Aoki Y. New BRAF knockin mice provide a pathogenetic mechanism of developmental defects and a therapeutic approach in cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Dec 15;23(24):6553-66. |
|
Costello Syndrome (OMIM#218040) Model Mice
The Costello syndrome model mice are knock-in mice carrying HRAS G12S mutation, which is found in approximately 80% of patients. HRAS is one of the small GTP-binding proteins present in RAS/MAPK signaling and is also known as a carcinogenic gene. In these strains, homozygous mice are embryonic lethal, and heterozygous mice show facial abnormalities, malocclusion, anal prolapse, cardiomegaly, and renal disease, similar to patients. In addition, abnormal energy metabolism is observed during a high-fat diet, which is attributed to alterations in mitochondrial β-oxidation pathway that produces energy from fatty acids. |
| Strain name: ▪ B6.Cg-Hras<tm1.1(G12S)Tumg> (C57BL/6 background, Neo+) (RBRC10866) ▪ C.Cg-Hras<tm1.1(G12S)Tumg> (C57BL/6 background) (RBRC11578) |
| References: [1] Katata Y, Inoue SI, Asao A, Kobayashi S, Terui H, Inoue-Shibui A, Abe T, Niihori T, Aiba S, Ishii N, Kure S, Aoki Y. Costello syndrome model mice with a HrasG12S/+ mutation are susceptible to develop house dust mite-induced atopic dermatitis. Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 13;11(8):617. [2] Oba D, Inoue SI, Miyagawa-Tomita S, Nakashima Y, Niihori T, Yamaguchi S, Matsubara Y, Aoki Y. Mice with an Oncogenic HRAS Mutation are Resistant to High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Exhibit Impaired Hepatic Energy Homeostasis. EBioMedicine. 2018 Jan;27:138-150. |
|
Noonan Syndrome (OMIM# 615355) Model Mice
The Noonan syndrome model mice are knock-in mice carrying RIT1 A57G mutation found in a subset of patients. RIT1 is one of the small GTP-binding proteins present in RAS/MAPK signaling and is also known as a carcinogenic gene. In these strains, homozygous mice are embryonic lethal, and heterozygous mice show embryonic edema, growth defects, facial abnormalities, anal prolapse, and cardiac hypertrophy, similar to patients. In addition, progressive cardiac fibrosis due to β-adrenergic receptor agonists has been reported. |
| Strain name: ▪ B6.Cg-Rit1<tm1(A57G)Tumg> (C57BL/6 background, Neo+) (RBRC10843) ▪ B6.Cg-Rit1<tm1.1(A57G)Tumg> (C57BL/6 background) (RBRC10844) |
| Reference: [1] Takahara S, Inoue SI, Miyagawa-Tomita S, Matsuura K, Nakashima Y, Niihori T, Matsubara Y, Saiki Y, Aoki Y. New Noonan syndrome model mice with RIT1 mutation exhibit cardiac hypertrophy and susceptibility to β-adrenergic stimulation-induced cardiac fibrosis. EBioMedicine. 2019 Apr;42:43-53. |
| Depositors | : | Yoko Aoki, M.D., Ph.D. and Shin-Ichi Inoue, Ph.D. Tohoku University |
|
| Keywords | : | RAS/MAPK signaling, CFC syndrome, Costello syndrome, Noonan syndrome, carcinogenic gene, intractable disease | |
| October2022 Saori Mizuno, Ph.D. Contact: Experimental Animal Division, RIKEN BioResource Research Center (animal.brc@riken.jp) All materials contained on this site may not be reproduced, distributed, displayed, published or broadcast without the prior permission of the owner of that content. |