|
September 2017 Mouse of the Month |
AQP4, the main subset of the aquaporin water channel family in the brain
C57BL/6N-Aqp4<tm1Tsna> (RBRC10054, flox)
|
|
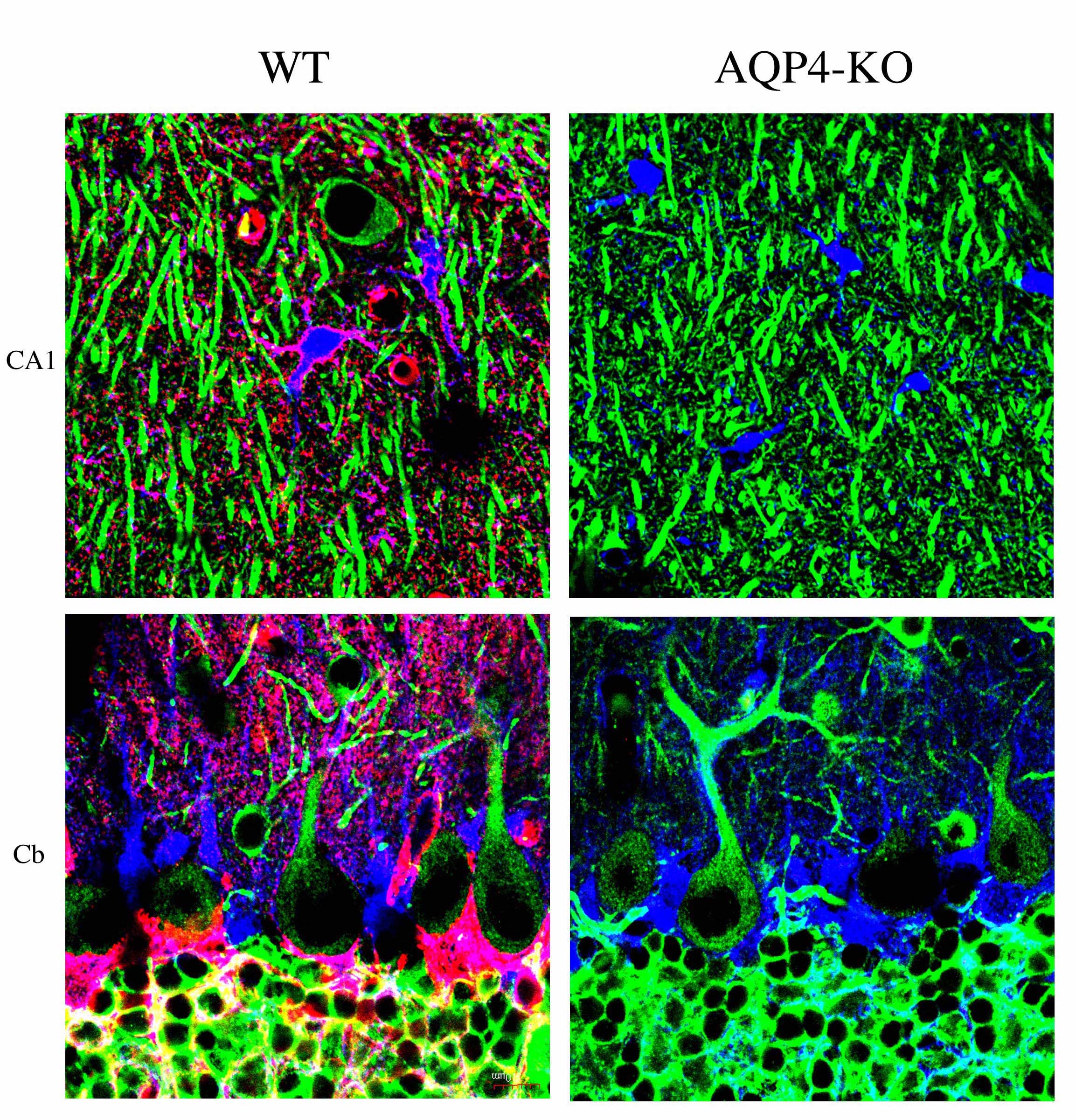
The aquaporin(AQP) family is a large collection of integral membrane proteins that enable the movement of water and other small, neutral solutes across biological membranes. Mammalian AQPs consist of 13 homologous members with varying degrees of similarity [1]. AQP4 is the main subset in the brain, particularly in glial astrocytes where it is highly expressed in the perivascular and subpial endfeet [2]. Terumitsu-Tsujita and her colleagues generated AQP4 knockout mice and observed a significant suppression of neural activity-dependent extracellular space volume change which is associated with astrocyte swelling [3]. They also found that water influx into the cerebrospinal fluid is regulated by AQP4 and not by AQP1, strongly supporting the idea that AQP4 regulates water homeostasis in the peri-capillary space [4]. Furthermore, they developed a PET ligand for AQP4 imaging based on TGN-020, a potent AQP4 inhibitor. Utilizing [11C]-TGN-020, PET images were successfully generated in wild type and AQP4 null mice [5]. |
| Depositor | : | Mika Terumitsu-Tsujita, Ph.D. Department of Functional Neurology and Neurosurgery Center for Integrated Human Brain Science, University of Niigata |
|
| Strain name | : | C57BL/6N-Aqp4<tm1Tsna> (flox mice) | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC10054 | |
| Strain name | : | C57BL/6N-Aqp4<tm1.1Tsna> (KO mice) | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC10053 | |
| References | : | [1] | Huber VJ, Tsujita M, Nakada T. Aquaporins in drug discovery and pharmacotherapy. Mol Aspects Med.; 33(5-6):691-703, 2012. |
| [2] | Nakada T. Virchow-Robin space and aquaporin-4: new insights on an old friend. Croat Med J.; 55(4):328-36, 2014. | ||
| [3] | Kitaura H, Tsujita M, Huber VJ, Kakita A, Shibuki K, Sakimura K, Kwee IL, Nakada T. Activity-dependent glial swelling is impaired in aquaporin-4 knockout mice. Neurosci Res.; 64(2):208-12, 2009. | ||
| [4] | Igarashi H, Tsujita M, Kwee IL, Nakada T. Water influx into cerebrospinal fluid is primarily controlled by aquaporin-4, not by aquaporin-1: 17O JJVCPE MRI study in knockout mice. Neuroreport; 25(1):39-43, 2014. | ||
| [5] | Nakamura Y, Suzuki Y, Tsujita M, Huber VJ, Yamada K, Nakada T. Development of a Novel Ligand, [C]TGN-020, for Aquaporin 4 Positron Emission Tomography Imaging. ACS Chem Neurosci.; 2(10):568-571, 2011. | ||
| September 2017 Contact: Shinya Ayabe, Ph.D. Experimental Animal Division, RIKEN BioResource Center All materials contained on this site may not be reproduced, distributed, displayed, published or broadcast without the prior permission of the owner of that content. |