|
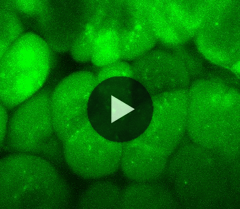
Autophagy monitoring congenic strains GFP-LC3#53 (RBRC00806)C.B6D2-Tg(CAG-GFP/LC3)53Nmz/Rbrc (RBRC01413)C3.B6D2-Tg(CAG-GFP/LC3)53Nmz/Rbrc (RBRC01414)MSM.B6D2-Tg(CAG-GFP/LC3)53Nmz/Rbrc (RBRC01227)Courtesy of Noboru Mizushima, M.D., Ph.D. |
| A | : | B6.B6D2-Tg(CAG-GFP/LC3)53NmzRbrc (RBRC00806), a donor strain in the C57BL/6JJcl to generate other three congenic lines. | |
| B | : | C.B6D2-Tg(CAG-GFP/LC3)53NmzRbrc (RBRC01413) in the BALB/cAnN. | |
| C | : | C3.B6D2-Tg(CAG-GFP/LC3)53NmzRbrc (RBRC01414) in the C3H/HeNCrlj. | |
| D | : | Live imaging of autophagosome in pancreatic tissues of B6-GFP-LC3 mice (RBRC00806). For imaging technology details, please refer Cao L et al. High Resolution Intravital Imaging of Subcellular Structures of Mouse Abdominal Organs Using a Microstage Device. PLoS ONE 2012. | |
|
Autophagy (Greek for “self-eating”) is known to have important roles in various physiological and pathological processes such as maintenance of the amino acid pool during starvation, preimplantation development, prevention of neurodegeneration, anti-aging, tumor suppression, clearance of intracellular microbes, and regulation of innate and adaptive immunity [1,2]. Accordingly, there is a growing need among scientists to be able to detect autophagy in vivo. The GFP-LC3#53 transgenic mouse is one of the most widely used in vivo autophagy monitoring tools and was developed by Dr. Noboru Mizushima [3]. This transgenic mouse enables the accurate detection of autophagosome in diverse biological processes. We have extended its capability to other useful inbred strains such as BALB/cAnN (RBRC00641), C3H/HeNCrlj, and MSM/MsRbrc (RBRC00209) by successive backcrossing. The genetic backgrounds of these strains were examined using simple sequence length polymorphism markers to assess congenic status. A genotyping protocol was also established to distinguish homozygous and hemizygous transgenic mice. These autophagy monitoring mice will be useful for assessing autophagy in various mouse disease models. |
| Depositor of donor strain | : | Noboru Mizushima, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology The University of Tokyo |
|
| What is autophagy? | : | http://www.cellcycle.m.u-tokyo.ac.jp/english/research/index.html | |
| Strain name | : | GFP-LC3#53 | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC00806 | |
| Strain name | : | C.B6D2-Tg(CAG-GFP/LC3)53Nmz/Rbrc | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC01413 | |
| Strain name | : | C3.B6D2-Tg(CAG-GFP/LC3)53Nmz/Rbrc | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC01414 | |
| Strain name | : | MSM.B6D2-Tg(CAG-GFP/LC3)53Nmz/Rbrc | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC01227 | |
| References | : | [1] | Mizushima N, Komatsu M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues.Cell 147(4):728-741, 2011. |
| [2] | Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Levine B.Methods in mammalian autophagy research.Cell 140(3):313-326, 2010. | ||
| [3] | Mizushima N, Yamamoto A, Matsui M, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y. In vivo analysis of autophagy in response to nutrient starvation using transgenic mice expressing a fluorescent autophagosome marker. Mol Biol Cell 15(3):1101-1111, 2004. | ||
|
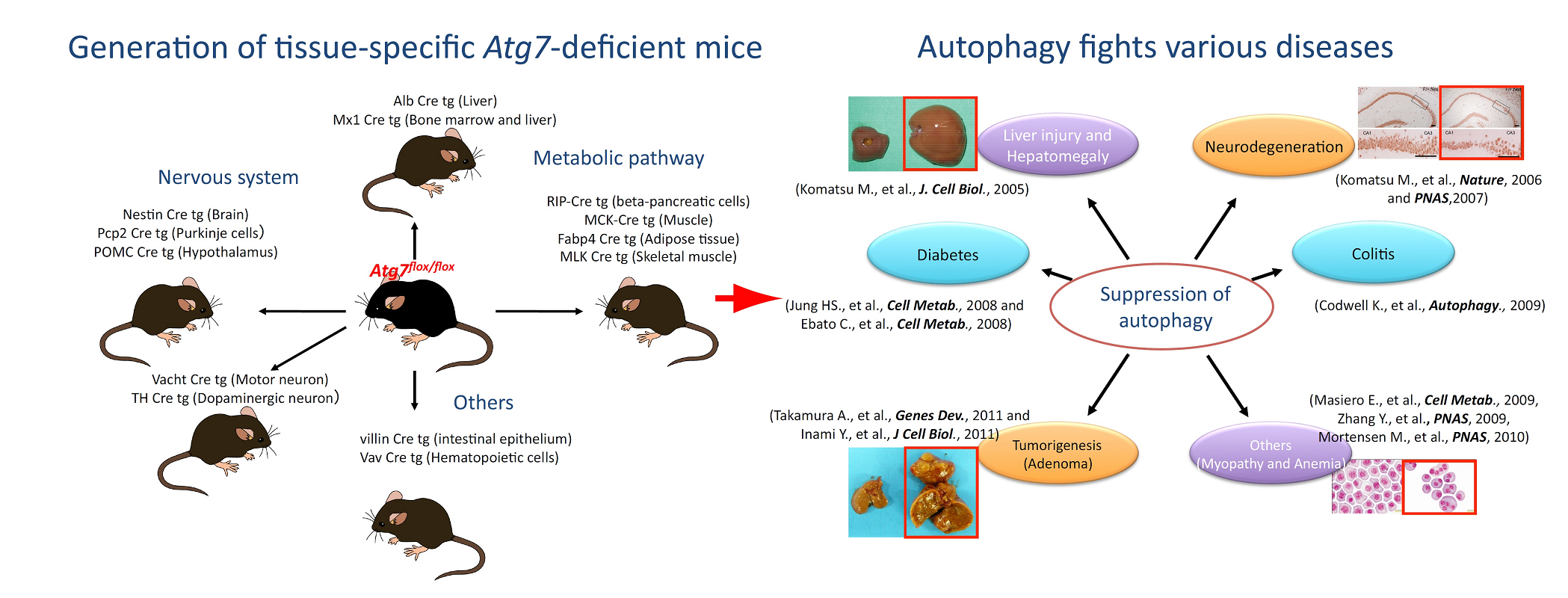
Atg7 deletion in various tissues B6.Cg-Atg7<tm1Tchi> (RBRC02759)B6.Cg-Atg7<tm1.1Tchi> (RBRC02760)Courtesy of Masaaki Komatsu, Ph.D. To investigate the physiological roles of autophagy in mice, conditional knockout mice for an autophagy-essential gene, Atg7, were generated. A number of groups have generated various tissue-specific autophagy-deficient mice. Many of the molecular mechanisms underpinning autophagy and the physiologic roles of these processes have since been elucidated. |
|
Autophagy is a pathway for bulk protein degradation that has been conserved in most eukaryotic cells. The initial steps of autophagy include the formation and elongation of the isolation membrane. This membrane enwraps organelles and other cytoplasmic components until forming a double-membrane vesicle called an autophagosome. The biogenesis of autophagosomes requires proteins encoded by autophagy-related (Atg) genes, most of which were initially identified in yeast. To date, Atg5 conditional knockout mice, GFP-tagged Map1lc3a Tg mice (mammalian homologue of Atg8p), and other various Atg-deficient mice have been established [1]. |
| Depositor | : | Masaaki Komatsu, Ph.D. Protein Metabolism Project Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Science |
|
| Strain name | : | B6.Cg-Atg7<tm1Tchi> | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC02759 | |
| Strain name | : | B6.Cg-Atg7<tm1.1Tchi> | |
| RBRC No. | : | RBRC02760 | |
| References | : | [1] | Mizushima N, Komatsu M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell; 147(4):728-41, 2011. |
| [2] | Komatsu M, Waguri S, Ueno T, Iwata J, Murata S, Tanida I, Ezaki J, Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y, Uchiyama Y, Kominami E, Tanaka K, Chiba T. Impairment of starvation-induced and constitutive autophagy in Atg7-deficient mice. J Cell Biol; 169(3):425-34, 2005. | ||
| [3] | Komatsu M, Waguri S, Chiba T, Murata S, Iwata J, Tanida I, Ueno T, Koike M, Uchiyama Y, Kominami E, Tanaka K. Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature; 441(7095):880-4, 2006. | ||
| [4] | Masiero E, Agatea L, Mammucari C, Blaauw B, Loro E, Komatsu M, Metzger D, Reggiani C, Schiaffino S, Sandri M. Autophagy is required to maintain muscle mass. Cell Metab; 10(6):507-15, 2009. | ||
| October 2016 Contact: Shinya Ayabe, Ph.D. Experimental Animal Division, RIKEN BioResource Center All materials contained on this site may not be reproduced, distributed, displayed, published or broadcast without the prior permission of the owner of that content. |